Introduction
In today's world, you can text/call/video call a person on the other side of the world in no time, and it is not even something unusual, Internet has become such an integral part of our lives. In this blog let's deep dive more into the Internet and understand how it works.
What is the Internet?
In simple terms, the Internet can be defined as a NETWORK OF NETWORKS. It is a global system of interconnected devices/computer networks which facilitate communication between each other via wired or wireless mediums.
Data Transmission
Well, there are various ways to transmit data from one place to another, It can follow a Guided media path (Wires: Copper wires, Optical fibers) or an Unguided path (Through Air: Radio waves, IR waves, EM waves etc)
The optimum way to transfer data would be through Optical Fibers. One more notable way of establishing communication would be Satellite communication but it also comes with a certain drawback in the distance the data should travel. The satellites in the geostationary orbit are about 36,000 KM away from earth, hence this is not the best way for data transfer although it is used in certain telecommunication systems.
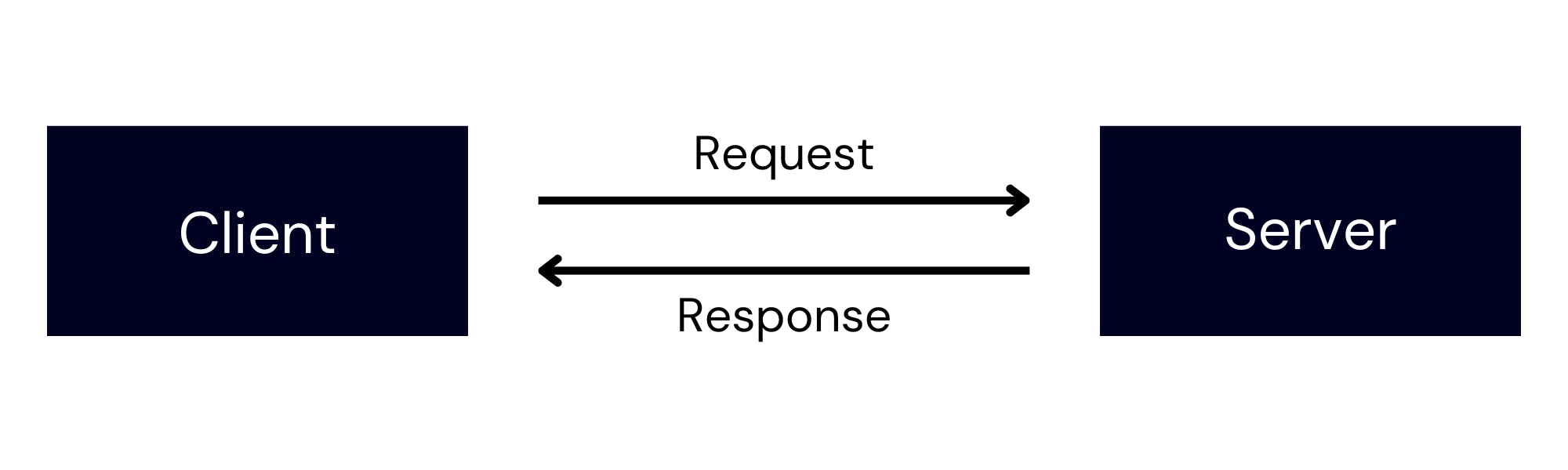
Working: The Client-Server Model
The Client-Server model explains how the internet works at its very basic level, let's say you are browsing something through your web browser, maybe a site like Amazon.com. As you search for Amazon.com, there is a request made to access the information. This request is then sent to the servers present in Amazon's data center and thus once it is approved the information requested is sent back. In this case, the device in which you are browsing is referred to as the CLIENT and the Amazon server is referred to as a SERVER.
Internet is not dependent on a single machine, Any two devices that can transmit and receive data between each other can be a part of a larger network, the internet for instance.
IP Address, Packets & Protocols
IP Address:
By now you might be wondering, how will the data be sent to the device which has requested data and not to any other device which is also connected to the Internet. This is done with the help of IP (Internet Protocol) ADDRESSES. IP Address is unique for every other device. Each device comes with a specific IP Address, be it your mobile phone, your laptop, your router or your modem. IP Address is usually provided by your ISP-Internet Service Provider. The server from which you're trying to access data also has a unique IP Address.
But how to remember all these IP Addresses? let's say you want to access data from google does that mean you should remember the IP Address of google? (8.8? 8.8. 8.8 is the primary DNS server for Google DNS)
NO, This is where DNS comes into the picture, DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is a like a logbook for the IP Addresses of all sites. We have to just remember the domain names which we are already familiar with. Some domain name examples are Google, Amazon, Youtube, Hashnode etc.
Packets:
The packet is a smaller segment of a larger message/data. The packet contains something called a "header", which contains the information about the data, which tells the receiving device what is the work of this particular packet. When the data is sent over the Internet it is broken into small fragments called packets/bits which are then routed by various routers and modems to reach the destination properly. Once the packets reach the receiver the packets are rearranged and there is a check done for any errors or missing bits if everything is clear then the data is delivered providing a seamless experience for the user.
Protocols:
The protocol is nothing but a set of rules; Two computers communicating have different hardware & software configurations, to establish a connection between them and facilitate communication we make use of protocols.
There are various protocols for many different purposes, namely:
TCP/IP -To send/receive packets in the right order
UDP- for video conferencing or streaming video.
HTTP- to access the web data.
Conclusion
The Internet- the term we use every other day is nothing but just a web of connected devices which facilitate communication between them. Data is transmitted in the form of packets over a particular protocol depending on the need. IP Address is unique to each device or server and helps in identifying the server or the device.
The Internet is just a deep dive into networks. which helps us understand how every device in the world is connected to one global network.
